Click the arrow to see the next slide with the correct interpretation.
Left-Sided Hearing Loss
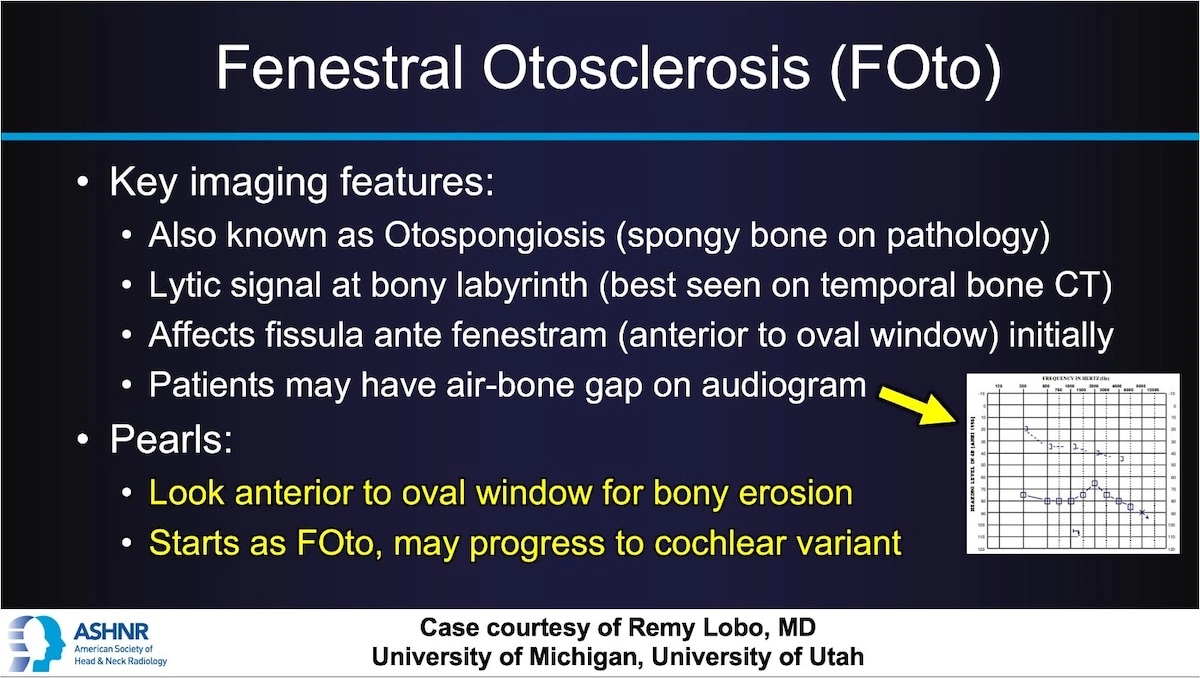
This case focuses on a patient presenting with left-sided hearing loss, ultimately diagnosed as fenestral otosclerosis (FOto) — a common cause of conductive hearing loss in adults.
Imaging Overview:
-
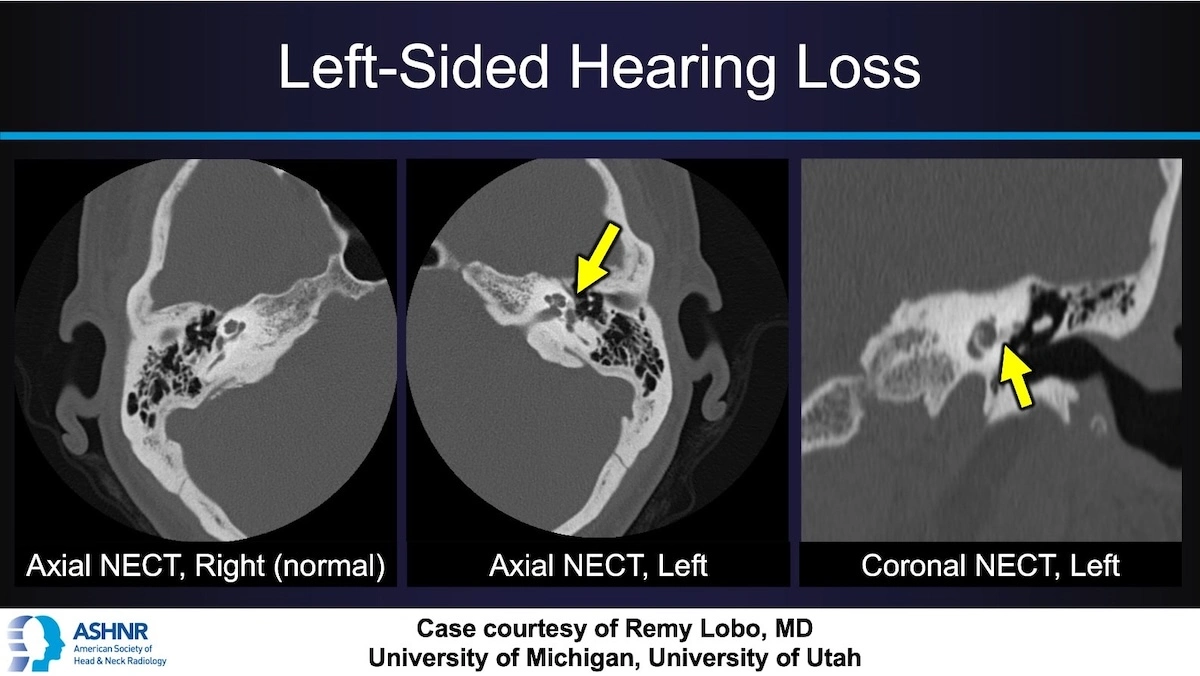
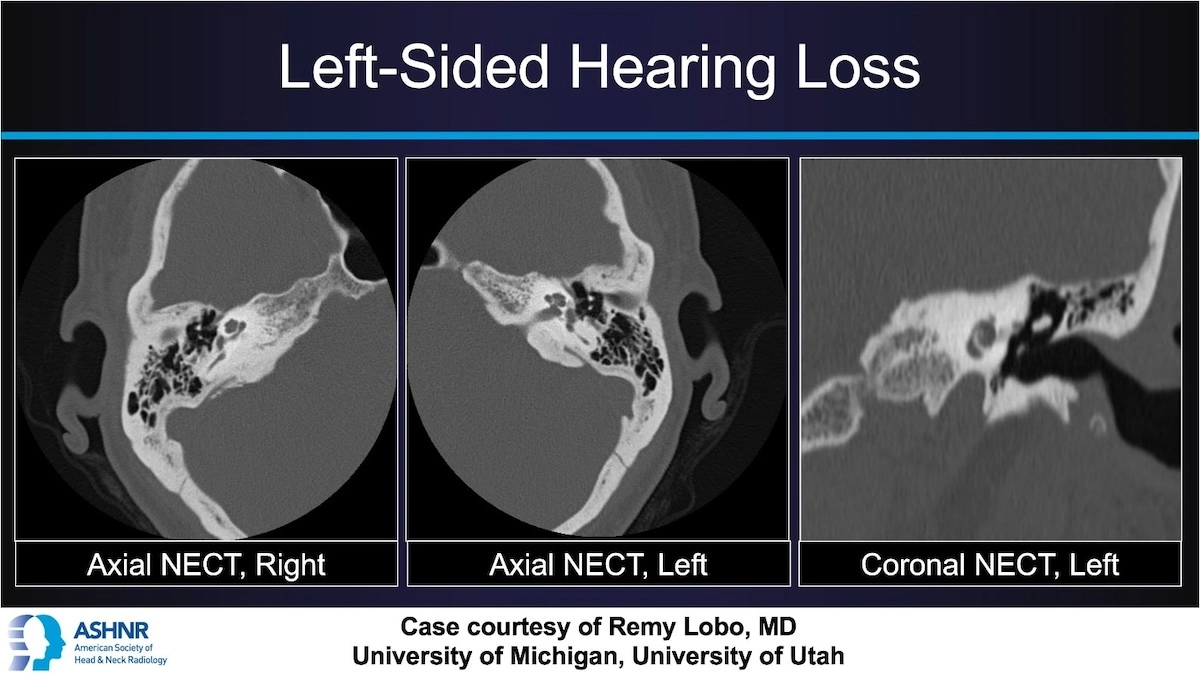
Axial and coronal NECT scans of the temporal bones demonstrate:
-
Normal right side
-
On the left side, a lytic focus anterior to the oval window, localized at the fissula ante fenestram
-
-
This lucent lesion represents early otospongiosis, where normal dense bone is replaced with spongy bone.
Clinical Insight:
Fenestral otosclerosis is a form of primary bone dysplasia that affects the otic capsule, particularly near the oval window. This causes stapes fixation, impeding sound transmission. Audiometry may reveal a conductive hearing loss with air-bone gap. If untreated, it may advance to the cochlear (sensorineural) form.
Case courtesy of Remy Lobo, MD
University of Michigan, University of Utah